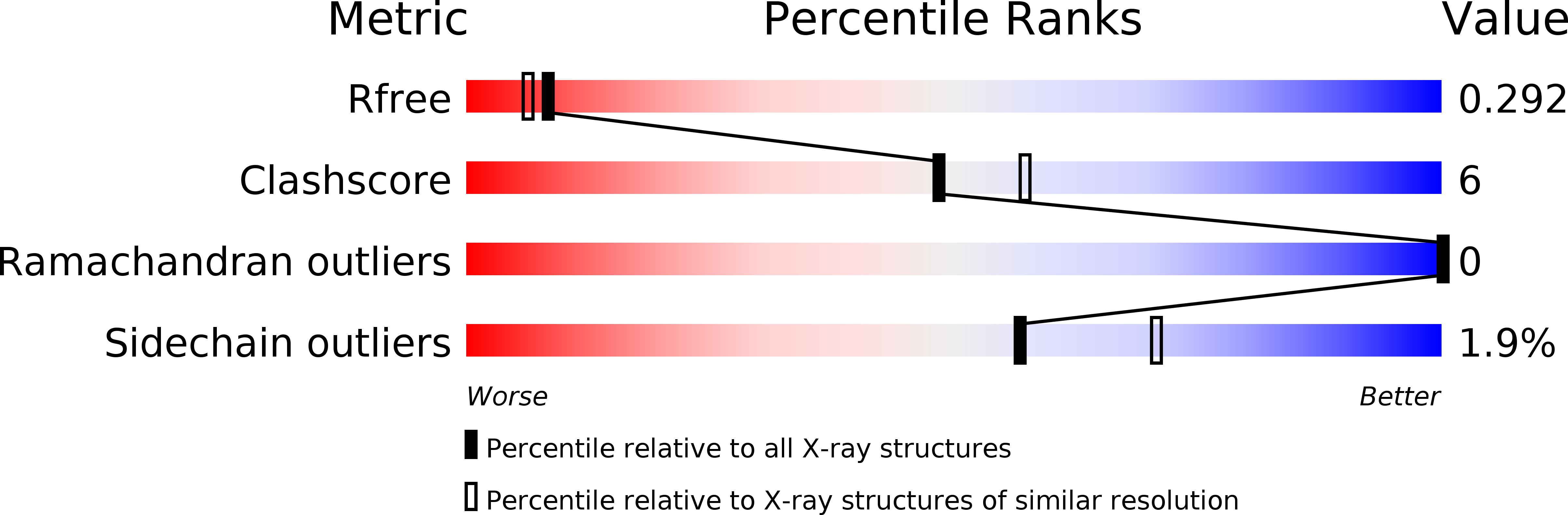
Substrate-Binding Mechanism of a Type I Extradiol Dioxygenase.
Cho, H.J., Kim, K., Sohn, S.Y., Cho, H.Y., Kim, K.J., Kim, M.H., Kim, D., Kim, E., Kang, B.S.(2010) J Biol Chem 285: 34643
- PubMed: 20810655
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.130310
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2WL3, 2WL9 - PubMed Abstract:
A meta-cleavage pathway for the aerobic degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons is catalyzed by extradiol dioxygenases via a two-step mechanism: catechol substrate binding and dioxygen incorporation. The binding of substrate triggers the release of water, thereby opening a coordination site for molecular oxygen. The crystal structures of AkbC, a type I extradiol dioxygenase, and the enzyme substrate (3-methylcatechol) complex revealed the substrate binding process of extradiol dioxygenase. AkbC is composed of an N-domain and an active C-domain, which contains iron coordinated by a 2-His-1-carboxylate facial triad motif. The C-domain includes a β-hairpin structure and a C-terminal tail. In substrate-bound AkbC, 3-methylcatechol interacts with the iron via a single hydroxyl group, which represents an intermediate stage in the substrate binding process. Structure-based mutagenesis revealed that the C-terminal tail and β-hairpin form part of the substrate binding pocket that is responsible for substrate specificity by blocking substrate entry. Once a substrate enters the active site, these structural elements also play a role in the correct positioning of the substrate. Based on the results presented here, a putative substrate binding mechanism is proposed.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the School of Life Science and Biotechnology, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 702-701, Korea.